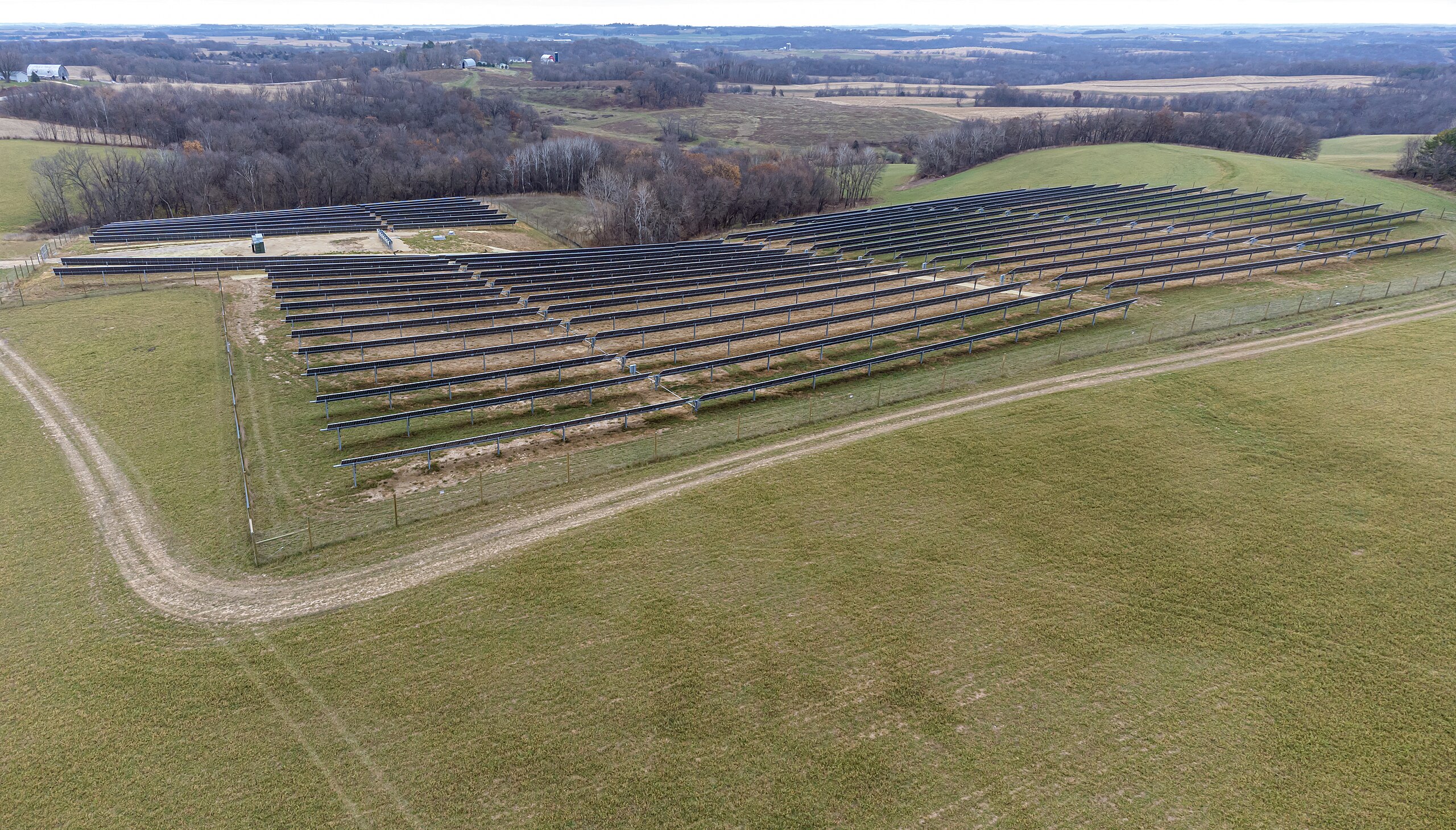
A newly published study examining property values near dozens of large Midwest solar farms has found no significant negative impact – and even a slight positive effect – from the projects, according to the data.
Loyola University researcher Gilbert Michaud has attended scores of community meetings about proposed solar projects, from the Midwest to rural France. In past research, he quantified that property values were the most common concern brought up in local hearings about proposed utility-scale solar in Europe — and he’s seen similar trends in the U.S.
And while solar arrays may have an aesthetic impact, property values are influenced by a wide range of other factors, such as the quality of schools and the local economy.
“I’ve observed a lot of the negative comments framed as ‘I think’ or ‘I saw something on social media,’” said Michaud, an assistant professor of environmental policy at the School of Environmental Sustainability at Loyola University Chicago. So he sought to “elevate the discussion from ‘I think, I think, I think,’” by injecting it with some hard data.
His latest study, published in the December 2024 issue of the journal Solar Compass, looked at property values surrounding 70 utility-scale solar projects in the Midwest and found they actually had a minor positive effect — increasing values 0.5% to 2%.
“While the impact itself — of a few thousand dollars — might not be incredibly meaningful,” said Michaud, “clearly these projects drive economic development in rural communities, through jobs, tax contributions, etcetera, which in turn increase residential property values.”
Emotions running high
Michael Wildermuth, a landowner in Allen County, Ohio, was hoping to lease land to the proposed 300 MW Birch Solar farm. But the project was denied by a state siting board, in the face of opposition from some residents.
“The nearest neighbors became enraged so quickly and voiced their rage so loudly that others were placed in a reactionary mode,” Wildermuth said. “The neighbors were greatly concerned with property values and flooding. The landowners were afraid of these vocal neighbors, the public officials were afraid of being on the wrong side of a political ‘hot potato’ issue.”
The developer appealed to the Ohio State Supreme Court, and Wildermuth filed an amicus brief. He wishes more data about property values had been available during the debate. He also thinks opponents ignored the $81 million the developer estimated it would contribute to the economy, and assumed the project would have little local economic benefit since the power would go to an Amazon facility.
“Just get people ‘all het up’ and you don’t have to deal with reason and facts,” Wildermuth said.
“Do I think solar farms could actually improve property values or the financial well-being of landowners and neighbors of solar farms? Yes, I do. We argued that. We also pointed out that, in the rural area where the farm was planned, the properties would remain stable for 30 years,” preventing them from being developed for other purposes that neighbors may find less desirable.
Shining new light
The study, co-authored by Loyola graduate Sampson Hao, notes that the benefits of rooftop solar on energy bills and property values are well-documented. But less is known about how utility-scale solar farms impact nearby properties — even though utility-scale solar accounts for about three-quarters of new solar development.
The study reviewed 70 solar farms built in the Midwest between 2009 and 2022, from a database by Berkeley Laboratory including solar farms over 5 MW. Hao and Michaud analyzed property values compiled by real estate firm Zillow, comparing values five years before a solar project became operational, with values at the operational date, which is often about two years after construction starts.
They aggregated by zip code, and controlled for factors like the COVID-19 pandemic that could affect housing values in a given year. Three-bedroom houses were used as a measure of overall property values. They also analyzed “control group” zip codes near the solar farm zip codes, but without solar farms, to account for other factors that might affect property values.
Michaud noted that while the number of bedrooms and other factors have a much larger impact on property values, the small positive impact that nearby solar farms could have could be similar to that of cultural amenities, like arts centers. Solar farms can also have an impact on schools — a major factor in determining property values — since solar projects augment local tax bases. Solar developers also often make ongoing contributions to school districts in the form of donations, supplies and energy education opportunities.
The study showed high numbers of solar farms going online in 2017 and 2021, with a smaller spike in 2020.
The projects included in the study range from a 10 MW urban installation in Chicago, installed by Exelon in 2010, to the 268 MW Riverstart Solar Park in Indiana, from 2021. Only 11 of the 70 projects studied were over 100 MW in capacity. Indiana had the most arrays at 22, followed by 14 in Minnesota, eight in Michigan and seven in Illinois.
The most beneficial impact on property values was from solar farms between 5 and 20 MW in size, perhaps in part because these can be hidden by vegetative buffers.
“The paper is not about a house that’s 200 feet away from a solar project, that’s very rarely the case,” said Hao, noting that developers often offer to buy properties at above market value in such situations. “We wanted to look at a bigger scale. A project between 5 and 20 MW, you’re really not supposed to even see these with your bare eyes.”
Midwestern focus
Michaud said that debunking myths around solar farms is particularly important in the Midwest, where there is much untapped potential for solar. While it has less sun than the Southeast and California, which have led the nation in solar farm development, the Midwest has massive stretches of agricultural land where solar can be deployed along with crops.
“This is a really important finding for Midwestern government officials, land owners, and many others to know about,” Michaud said. “Many of these folks are now making decisions about whether to host a large-scale solar project in their community, and the potential impacts to property values is often something that comes up in local debates and at local hearings. Data can help tell a story and move the debate beyond anecdotal or subjective arguments.”
The Loyola study cites a 2018 analysis of 956 specific solar farms by a University of Texas researcher that found no conclusive evidence of impact on property values one way or another. The Loyola researchers also noted a study by Berkeley Laboratory that found about a 1% decline in property values around 2,000 solar farms in six states on the east and west coasts and in Minnesota.
“Most Midwestern states have 10 to 20 gigawatts of potential utility-scale solar in their queue, and developers are coming off of the coasts where the grid is more congested and there is less land for development, targeting agricultural land in the center of the country,” Michaud said. “Finding a large plot of land with good solar irradiation and access to a substation is the sweet spot for a lot of solar developers, and in essence, positive attributes of farming crops in the Midwest are also positive attributes for farming ground-mounted, large-scale solar.”
Perception becomes reality
The study notes the irony that perception plays a significant role in determining property values, and fears about property value declines can become a self-fulfilling prophecy.
“Projection and speculation drive market forces,” Michaud said. “A farmer might be angry that a solar farm is going in the community, he’s going to sell and move to Florida. A buyer thinks, ‘maybe I can negotiate this price down,’ and the house sells for less than its value, and an appraiser looks at that. But none of this is real, it’s just based on speculation and emotion, which then drives data points … it all started with an emotional response.”
Hao theorized that developers who make poor choices in siting and managing solar farms can have an impact on property values elsewhere, if negative stories about solar spread by word of mouth or social media.
“Is a developer doing their best to have as much of a buffer as economically feasible?” he asked. “Is the developer making vegetative screenings so you’re not going to see millions of panels? Is the developer doing their best to move the inverter to the center of the leased land so noise doesn’t get over the road? There’s a lot of things at the end of the day that developers can do better. It’s up to the developers to really step up their game to eliminate those potential negative effects.”
The Loyola study notes that solar developers often do things like hosting county fairs or supporting local organizations that can increase property values. Michaud said it’s possible such dynamics were reflected in their data showing small increases in property values, along with other benefits.
“From an economic perspective,” Michaud said, “locals should increasingly look at these data to understand the job opportunities, wages paid, new tax revenues and negligible or positive impacts on property values, and realize that large-scale solar projects might actually be an amenity in their community.”