Citizens assume wind or the sun powers most renewable energy equipment. However, generators rely on more resources, including plants. Organic matter influences renewable electricity’s development and generative potential more every year. Research and development continue to find innovative ways to incorporate natural assets into utilities, making them the most sustainable they have ever been.
1. Hydropower
Plant matter transforms when used to produce green power. Processing could turn it into a slurry or wood chips, and the latter is suitable for burning. Hydropower turbines use steam to keep spinning. This is a versatile method of renewable energy that is useful for hydropower-specific plants or biomass producers.
Plants are also an underutilized source of energy storage. Hydraulics may be intermittent, and nature is designed to store water, sending what it holds to underground reservoirs. What the plants keep is essential for increasing the dependability of hydropower.
2. Biogas Production
Waste-to-energy is an expansive and emerging market, using plants and other organic materials to make biogas. This happens via anaerobic digestion, which may convert into heat or cool connected structures. Operators can send materials to combustion engines or turbines.
Temperature regulation and capturing thermal runaway are metrics factories are always refining, and plants are powerful tools for keeping indoor and outdoor temperatures controllable amid climate change. Facilities may utilize landscaping and natural shade around plants to increase productivity and energy consumption.
Steam produced in biogas facilities may remain in that form, or technicians can chill it, turn into a liquid and store it for alternative uses. This is one of the most expensive and energy-intensive aspects of biogas because the energy required for the chillers is notable.
3. Biomass Energy
Biomass energy is the most apparent instance of plants influencing renewable utilities. Corn, sugar cane, switchgrass and more can create biofuels — competitive replacements for fossil fuel-based solutions like ethanol and diesel. The technology supports electric vehicles (EVs) and buildings.
It is one of the most versatile renewable power sources on the market. Biomass-generating window panes flourish on skyscraper siding, and wastewater plants leverage bacteria to repurpose contaminants from the treatment process. Farmers may also save on electric and fuel bills by using biomass as compost, boosting crop health and strength. This leads to fewer chemicals, resources and equipment for maintaining the property.
Households are doing everything they can to live more sustainably, whether building a sunroom, weatherstripping or installing a biomass boiler. The feedstocks can go into these boilers to heat a house as pellets. Non-renewable resources power 60% of U.S. utilities, so transitioning to plant-based avenues is critical for achieving national climate objectives.
4. Windbreaks and Wind Turbines
Plants do not always provide a source of electricity, but they often encourage other technologies to maximize their potential. Smart vegetation management — like maintaining buffers and keeping electrical areas clear — will empower the turbines instead of weakening them.
Towering wind turbines want as much force to hit them as possible while preventing damage. Trees and other deep-rooted plants are the ideal defense and windbreak to stop turbine destruction.
5. Agrivoltaics
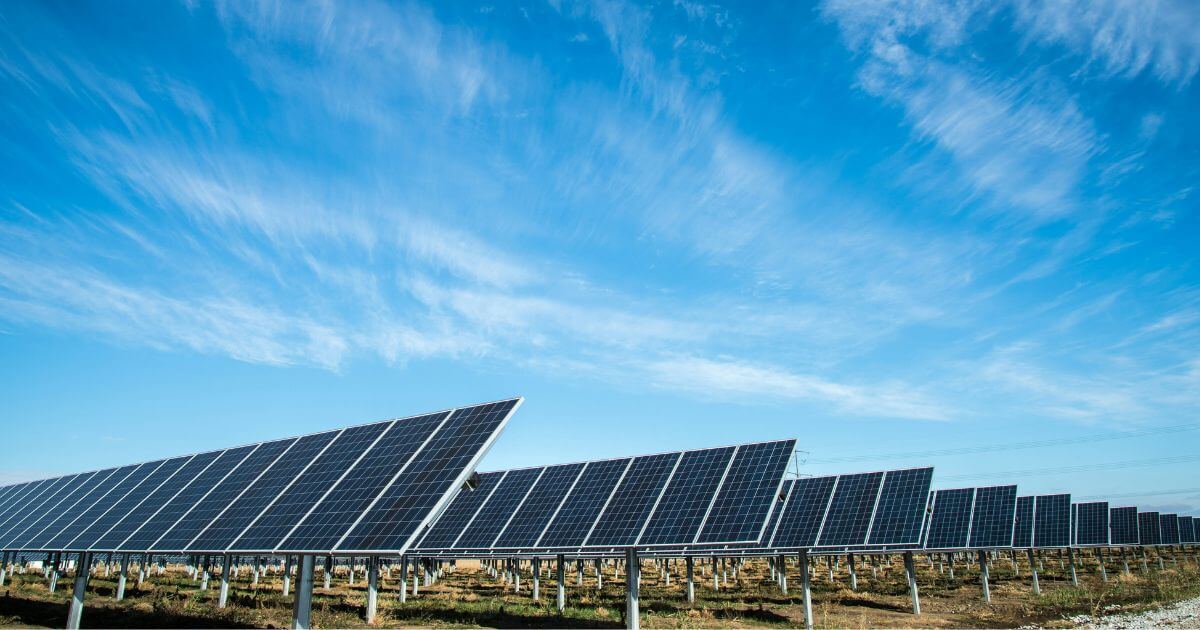

Agrivoltaics enhance agricultural production by increasing crop shade and protection with solar panels. More flowers and plants are willing to grow in these conditions as opposed to full sun. This invites more pollinators to the area, keeping the plants supplied with nutrients for healthy growth cycles.
The plants — including shade-tolerant leafy greens — keep the solar panels cool. It makes the panels 10% more productive in the perfect symbiotic relationship. This will reduce the property’s energy needs and water consumption, making it even more optimized as a clean generator.
6. Carbon Sequestration
Carbon emissions increase global temperatures, making the world use more electricity than it should. Ballooning power demands and population growth make striking a balance even more challenging. Long-term energetic stability requires plants to sequester carbon.
The Amazon Rainforest can capture 150 billion metric tons of carbon despite deforestation efforts. Its plant density is so vital to maintaining temperatures that it is one of the climate tipping points identified by climate scientists.
Not every region needs to be as covered in plants as the Amazon, but eliminating them for urbanization or industrialization harms power generation. Intermittent renewable sources will not be able to be reliable without the assistance of carbon-sequestering plants.
7. Phytoremediation
Utilities leave their mark even after shutting down. Brownfields and other contaminated areas where fossil fuel operations once stood need healing from the pollutant density. Plants are a solution for long-term renewable elecricity expansion if green power finds new homes in these defunct power facilities through phytoremediation.
Some plants can absorb specific pollutants, healing contaminated waters and soil. This would allow a clean power plant to move in, upcycling the fossil fuel infrastructure already there. Doin so reduces operational costs by preparing the site beforehand, setting it up for success. The process could also reinforce soil again to be better for grounding turbines or panels where it was previously unstable or unsafe for humans to maintain in person.
8. Plant-Based Batteries
From lithium-ion to solid-state, batteries are going through massive developments. This is notable for the EV industry, but grid modernization also needs strong batteries for energy storage. Plant-based alternatives are in the research stages, using cellulose or lignin to make them some of the most sustainable blueprints in history.
They are naturally abundant and renewable resources that introduce a new line of materials feeding into green battery technology, specifically for anodes. Reducing reliance on mining for precious metals will make the grid’s transformation more seamless and EV life cycle assessments more eco-conscious.

Supporting Plant Power
Humans focus on the heavy metals and electricity running through renewable power machinery, yet plants could drive their success. Green electricity forces humanity to look back to nature to develop a more positive relationship with energy use and creation. Looking past power plants into sprawling grass fields is the natural next step in capturing as much potential as possible as humanity attempts to reverse the climate crisis.